Abstract
Background:The role of radiation therapy (XRT) for advanced stage Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) is controversial. In the HD15 trial, the German Hodgkin Study Group (GHSG) administered XRT for PET-positive residual disease ≥2.5 cm at least 2 weeks after completion of chemotherapy and showed 91.5 % in-field control rate with a median follow-up of 102 months (Engert, A; personal communication). However, there is no comparison arm where patients with PET-positive residual disease ≥2.5 cm did not receive XRT. SWOG S0816 was a US intergroup trial utilizing ABVD-based therapy with response adaptation based on interim PET imaging; XRT was not allowed per protocol, and counted as an event. In this analysis, we identified patients in S0816 who would have met HD15 criteria for XRT, but did not receive XRT per design. We then modeled the potential impact of XRT on disease control.
Patients and Methods:Of 336 eligible and evaluable HIV-negative patients enrolled in S0816, 49 had an end-of-treatment PET (termed "PET3," to be done 6-8 weeks after completion of chemotherapy) that was positive (i.e. Deauville 4-5) upon central review. We simulated the progression free survival (PFS) if XRT had been delivered per HD15 criteria (PET positive disease and ≥2.5 cm), evaluating by assumptions of 50, 80 and 90% control of the disease within the XRT fields. Receiver operating characteristics (ROC) analyses were performed with additional size cut-off points of 2.0 and 1.5 cm.
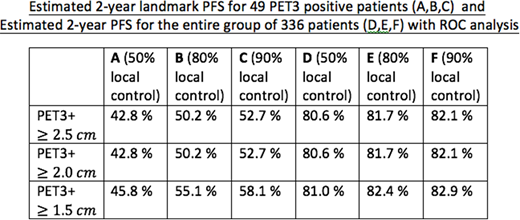
Results:The median follow-up for the 49 PET3 positive patients was 71 months (range 9.7-92.6). For these 49 patients, the observed landmark PFS at 2 years after the date of PET3 was 30.6%. Twenty-four (49%), 33(67%), and 40 (82%) of the 49 patients had at least one site of disease that met the HD15 criteria for XRT with ≥2.5 cm, ≥2.0 cm, and ≥1.5 cm size cut-offs respectively. Sixteen, 19, and 25 patients had disease progression respectively from each group at median of 1.4-1.5 months. Twelve, 12, and 15 patients had relapses limited to the sites that would have been radiated following HD15 criteria with ≥2.5 cm, ≥2.0 cm, and ≥1.5 cm respectively. Estimated landmark PFS at 2 years for the 49 PET3 positive patients assuming 50, 80, and 90 % control of the disease within the radiated sites following HD15 guideline with ≥2.5 cm, ≥2.0 cm, and ≥1.5 cm cut-off are summarized in columns A, B, and C of the table respectively. For the entire group of 336 patients, the observed PFS at 2 years was 79%. Estimated 2-year PFS for the entire group of 336 patients assuming 50, 80, and 90 % control of the disease within the radiated sites following HD15 guideline with ≥2.5 cm, ≥2.0 cm, and ≥1.5 cm cut-off are in columns D, E, and F of the table respectively.
Conclusion: Among the PET3 positive patients, consolidation XRT per HD15 criteria with cut-off points of 2.5, 2.0, and 1.5 cm could have raised the 2-year PFS by 12-28 % assuming 50-90% local control within radiated sites. However, the improvement in PFS is more moderate at 1.6-3.9 % if we consider the entire cohort of 336 patients. Although there may be some gain in PFS as the cut-off point is lowered by our ROC analysis, one needs to consider the trade-off against potentially increasing normal tissue toxicity as more sites are irradiated.
Brem:Pharamcyclics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Genetech: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene: Speakers Bureau; Bayer: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Bartlett:Merck & Co: Research Funding; Forty Seven: Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding; Immune Design: Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; ImaginAB: Research Funding; Janssen: Research Funding; KITE: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Acerta: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pfizer: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; Millennium: Research Funding; Genentech: Research Funding; Astra Zeneca: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Research Funding; Gilead: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Bristol-Meyers Squibb: Research Funding; Affimed: Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Research Funding. Evens:Seattle Genetics, Inc.: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Affimed: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy; Tesaro: Research Funding; Bayer: Consultancy; Acerta: Consultancy; Pharmacyclics International DMC: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Abbvie: Consultancy. Rimsza:NanoString: Other: Inventor on the patent for the Lymph2Cx assay. Leonard:Novartis: Consultancy; Celgene: Consultancy; MEI Pharma: Consultancy; AstraZeneca: Consultancy; ADC Therapeutics: Consultancy; United Therapeutics: Consultancy; BMS: Consultancy; Biotest: Consultancy; Sutro: Consultancy; Karyopharm: Consultancy; Juno: Consultancy; Gilead: Consultancy; Genentech/Roche: Consultancy; Pfizer: Consultancy; Bayer: Consultancy. Kahl:Seattle Genetics: Consultancy; Genentech: Consultancy; Acerta: Consultancy; AstraZeneca: Consultancy; Abbvie: Consultancy; ADC Therapeutics: Consultancy; CTI: Consultancy; Gilead: Consultancy; Juno: Consultancy; Celgene: Consultancy. Smith:BMS: Consultancy; Portola: Honoraria. Friedberg:Bayer: Honoraria.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.